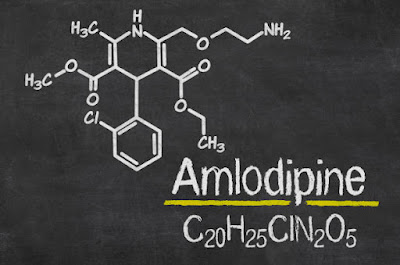
Amlodipine:
Introduction to Amlodipine
Amlodipine is a medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and chest pain (angina). It belongs to a class of drugs known as calcium channel blockers, which work by relaxing blood vessels to improve blood flow and reduce the workload on the heart.
Mechanism of Action
Amlodipine works by blocking calcium channels in the heart and blood vessels. By inhibiting the influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells, it dilates coronary and peripheral arteries, leading to decreased vascular resistance and increased blood flow. This mechanism helps reduce blood pressure and relieve angina symptoms.
Uses and Indications
The primary indication for amlodipine is the treatment of hypertension. It is also used alone or in combination with other medications to manage chronic stable angina and variant angina. Additionally, amlodipine has been investigated for its potential benefits in other conditions such as Raynaud's phenomenon and congestive heart failure, although its use in these conditions is less common.
Dosage and Administration
The typical starting dose of amlodipine for hypertension is 5 mg once daily, with the option to increase to a maximum dose of 10 mg daily if necessary. For angina, the usual starting dose is 5 mg once daily, which may be increased to 10 mg daily based on response. Amlodipine can be taken with or without food and should be swallowed whole with a glass of water.
Side Effects
Common side effects of amlodipine include dizziness, flushing, headache, and peripheral edema (swelling of the ankles or feet). These side effects are usually mild and transient. However, some individuals may experience more serious adverse reactions such as hypotension, palpitations, or allergic reactions. Patients should seek medical attention if they experience severe or persistent side effects.
Precautions and Warnings
Amlodipine is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or its components. It should be used with caution in patients with severe aortic stenosis or hepatic impairment. Amlodipine may cause hypotension, especially in patients with volume depletion or those receiving concomitant treatment with other antihypertensive agents. Close monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate is recommended during initiation and dosage adjustment.
Drug Interactions
Amlodipine may interact with other medications, including beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and certain antibiotics. Concomitant use of these drugs may potentiate the hypotensive effects of amlodipine or increase the risk of adverse reactions. Patients should inform their healthcare providers about all prescription, over-the-counter, and herbal medications they are taking before starting amlodipine therapy.
Overdose
In the event of an overdose with amlodipine, supportive measures should be initiated, including gastric lavage, activated charcoal administration, and symptomatic treatment of hypotension and bradycardia. In severe cases, intravenous calcium infusion or vasopressor agents may be necessary to reverse the effects of calcium channel blockade.
Special Populations
Amlodipine can be used in pregnancy if the potential benefits outweigh the risks to the fetus. However, it should be avoided during breastfeeding due to limited data on its excretion in breast milk. Geriatric patients may be more susceptible to the hypotensive effects of amlodipine and may require lower initial doses. The safety and efficacy of amlodipine in pediatric patients have not been established.
Cardiovascular Benefits: Amlodipine's impact extends beyond hypertension and angina. It has shown effectiveness in preventing cardiovascular events, making it a crucial component in managing overall cardiovascular health. Studies indicate that Amlodipine reduces the risk of stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular complications, emphasizing its role in broader preventive strategies.
Patient Compliance and Adherence
Ensuring patient compliance is paramount in achieving the desired therapeutic outcomes. Amlodipine's once-daily dosing regimen enhances patient adherence, as it simplifies the medication schedule, making it more convenient for individuals managing chronic conditions. Improved adherence contributes significantly to better blood pressure control and reduced cardiovascular risks.
Emerging Research and Innovations Ongoing research explores novel applications and formulations of Amlodipine. Researchers are investigating its potential in treating vascular-related conditions such as migraines and Raynaud's phenomenon. Additionally, pharmaceutical advancements may lead to innovative formulations, offering alternative administration routes or improved efficacy, further expanding the medication's therapeutic scope.
Patient Education and Lifestyle Modifications
While Amlodipine is a valuable tool in cardiovascular management, patient education on lifestyle modifications remains crucial. Healthcare providers should emphasize the importance of a healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation alongside medication. This holistic approach empowers patients to actively participate in their cardiovascular health, complementing the benefits of Amlodipine.Global Impact and Accessibility Amlodipine's widespread use has contributed to its global impact on public health. Its affordability and accessibility make it an essential medication, especially in regions with a high prevalence of hypertension. The medication's availability has improved the management of cardiovascular diseases on a global scale, addressing a critical aspect of public health.
Innovative Formulations and Combination Therapies Pharmaceutical advancements have led to the development of combination therapies involving Amlodipine. Combining Amlodipine with other antihypertensive agents in a single pill simplifies treatment regimens and enhances efficacy. These combinations, tailored to individual patient needs, showcase the ongoing efforts to optimize cardiovascular care and improve treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Amlodipine stands as a cornerstone in the management of hypertension and angina, offering not only effective blood pressure control but also potential cardiovascular benefits. As research continues to unravel new facets of its pharmacology, Amlodipine remains a dynamic and evolving tool in the realm of cardiovascular medicine. Patients and healthcare providers alike can look forward to the ongoing innovations and advancements that contribute to the improvement of cardiovascular health worldwide.